- Deuterium Element
- Hydrogen Deuterium Singly Ionized Helium Cell
- Hydrogen Deuterium Singly Ionised Helium Atom
- Hydrogen Deuterium Singly Ionized Helium Chemical
In which of the following systems will the wavelength corresponding to n = 2 to n = 1 be minimum?
Options
Hydrogen atom
Deuterium atom
Singly ionized helium
Doubly ionized lithium
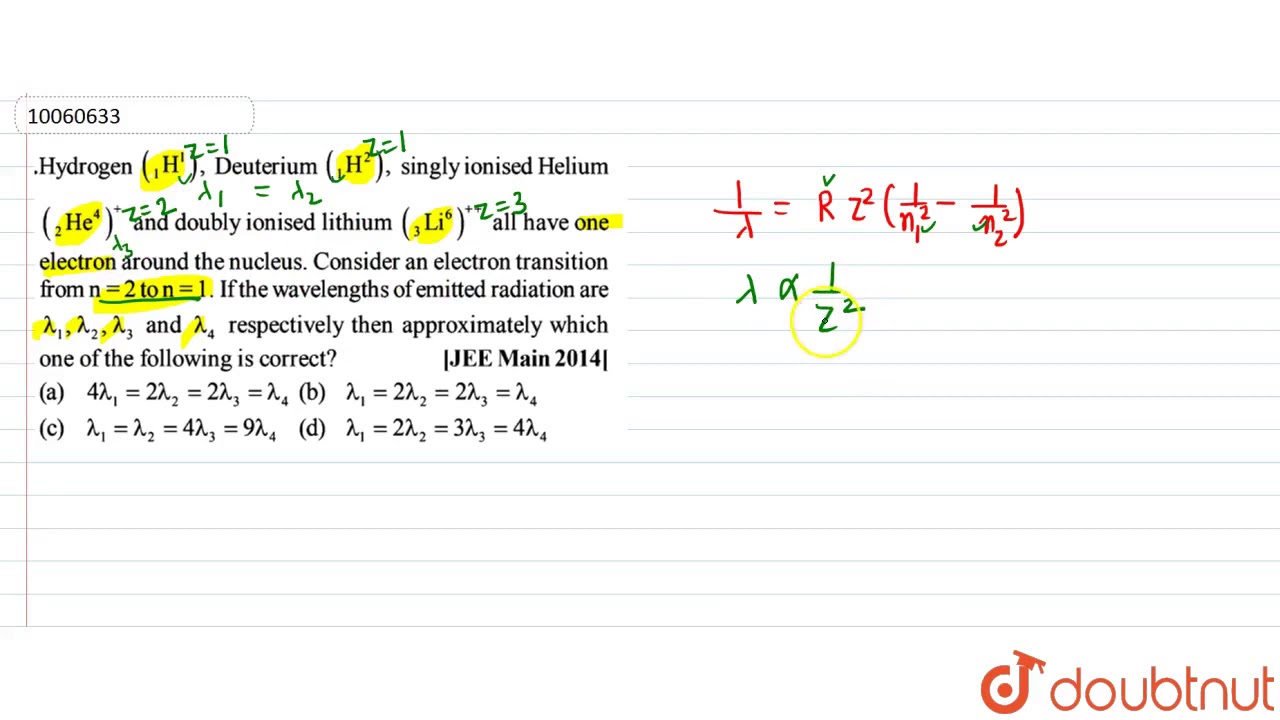
Hydrogen Deuterium singly ionised Helium and doubly ionised lithium all have one electron around the nucleus. Consider an electron transition from to. If the wavelengths of emitted radiation are and respectively then approximately which one of the following is correct? Hydrogen (H), deuterium (D), singly ionized helium (Het) and doubly ionized lithium (Li) all have one electron around the nucleus. Consider n=2 to n=1 transition. The wavelengths of emitted radiations are 2, 1, 2, and 2, respectively. Hydrogen, deuterium, and singly ionized helium are all examples of one-electron atoms. The deuterium nucleus has the same charge as the hydrogen nucleus, and almost exactly twice the mass.
Solution
Doubly ionized lithium
The wavelength corresponding the transition fromn2 to n1 is given by
`1/lamda =RZ^2 (1/n_1^2 - 1/n_2^2)`]
Here,
R = Rydberg constant
Z = Atomic number of the ion
From the given formula, it can be observed that the wavelength is inversely proportional to the square of the atomic number.
Therefore, the wavelength corresponding to n = 2 to n = 1 will be minimum in doubly ionized lithium ion because for lithium, Z = 3.
Video TutorialsVIEW ALL [2]
view
Video Tutorials For All Subjects
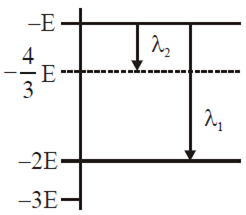
$lambda_1$ =$lambda_2 =4 lambda_3 = 9lambda_4$
B$4lambda_1 = 2lambda_2 = 2lambda_3 =lambda_4$
C$lambda_1 = 2lambda_2 =2 surd 2 lambda_3 = 3 surd 2 lambda_4$
$lambda_1 = lambda_2 =2lambda_3 =surd 2lambda_4$
Solution:
$Z_{1:}=:1,:Z_2:=:1,:Z_3:=:2:and:Z_4:=3.:$
$:frac{1}{lambda }:=:RZ^2left(frac{1}{1^2}:-:frac{1}{2^2}right):or:::::::lambda :=frac{4}{3RZ^2}:$
$:or:::::lambda Z^2:=:constant::$
$:So::lambda _1left(1right)^2:=:lambda _2:left(1right)^2:=:lambda _3left(2right)^2:=:lambda aleft(3^2right):$
$:or:lambda _1:=:lambda _1:lambda _2:=:4lambda _3:=:9lambda _{4.}$
1. When a metal surface is illuminated by light ofwavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum
velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and2v respectively.
The work function of the metal is(h - Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in air)
2. Two conducting shells of radius a and b areconnected by conducting wire as shown in figure.The capacity of system is :
3. When $_{92}U^{235}$ undergoes fission, 0.1% of its
original mass is changed into energy. How much
energy is released if 1 kg of $_{92}U^{235}$ undergoesfission
4. One mole of an ideal gas is taken from state A tostate B by three different processes,
(i) ACB (ii) ADB (iii) AEB as shown in the P-Vdiagram. The heat absorbed by the gas is.
5. In the formula$ X = 3 YZ^2, X $and Z have dimensions
of capacitance and magnetic induction respectively.
The dimensions of Y in MKSA systemare :
6. Two very long, straight, parallel wires carry steadycurrents I and -I respectively. The distancebetween the wires is d.
At a certain instant oftime, a point charge q is at a point equidistantfrom the two wires, in the plane of the wires.
Itsinstantaneous velocity v is perpendicular to thisplane. The magnitude of the force due to themagnetic field acting on the charge at this instantis.
7. Two projectiles A and B thrown with speeds in the ratio$ 1 :sqrt{ 2}$ acquired the same heights. If A is thrown at an angle of $45^circ$ with the horizontal, the angle of projection of B will be
8. A meter bridge is set up as shown, to determinean unknown resistance ‘X’ using a standard 10ohm resistor.
The galvanometer shows null pointwhen tapping-key is at 52 cm mark.
The endcorrectionsare 1 cm and 2 cm respectively for theends A and B.
The determined value of ‘X’ is
Deuterium Element
9. A disk of radius a / 4 having a uniformlydistributed charge 6 C is placed in the x - y planewith its centre at (-a / 2, 0, 0). A rod of length acarrying a uniformly distributed charge 8 C isplaced on the x-axis from x = a /4 to x = 5a / 4.
Two point charges - 7 C and 3 C are placed at (a/ 4, - a /4, 0) and (- 3a /4, 3a / 4, 0), respectively.
Consider a cubical surface formed by six surfaces$x = ± a / 2, y = ± a / 2, z = ± a / 2$. The electric fluxthrough this cubical surface is
10. A particle of mass m moving in the x directionwith speed 2v is hit by another particle of mass2m moving in the y direction with speed v. If thecollision is perfectly inelastic, the percentage lossin the energy during the collision is close to
1. The phase difference between displacement and acceleration of a particle in a simple harmonic motion is:
2. A cylinder contains hydrogen gas at pressure of 249 kPa and temperature $27^circ,C$. Its density is :$(R = 8.3,J,mol^{-1}K^{-1}$)
3. The solids which have negative temperature coefficient of resistance are :
Hydrogen Deuterium Singly Ionized Helium Cell
4. The energy equivalent of 0.5 g of a substance is:
Hydrogen Deuterium Singly Ionised Helium Atom
5. The Brewsters angle $i_b$ for an interface should be:
Hydrogen Deuterium Singly Ionized Helium Chemical
6. Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stop clock. A contains an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stop cock is suddenly opened. The process is:
7. A screw gauge has least count of 0.01 mm and there are 50 divisions in its circular scale.
The pitch of the screw gauge is:
8. For which one of the following, Bohr model is not valid?
9. A body weighs 72 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it, at a height equal to half the radius of the earth?
10. The refractive index of a particular material is 1.67 for blue light, 1.65 for yellow light and 1.63 for red light. The dispersive power of the material is .........
